Introduction
2024 is set to be the year of AI agents, marking a significant shift in how artificial intelligence systems are designed and implemented. AI agents differ from traditional monolithic models by incorporating modular components that enhance adaptability and performance. This document explores the evolution from standalone models to compound AI systems and the emergence of AI agents, detailing their reasoning, actions, and memory capabilities. We will also discuss the mathematical foundations that underpin these advancements.
Background: The Evolution of AI Systems
From Monolithic Models to Compound AI Systems
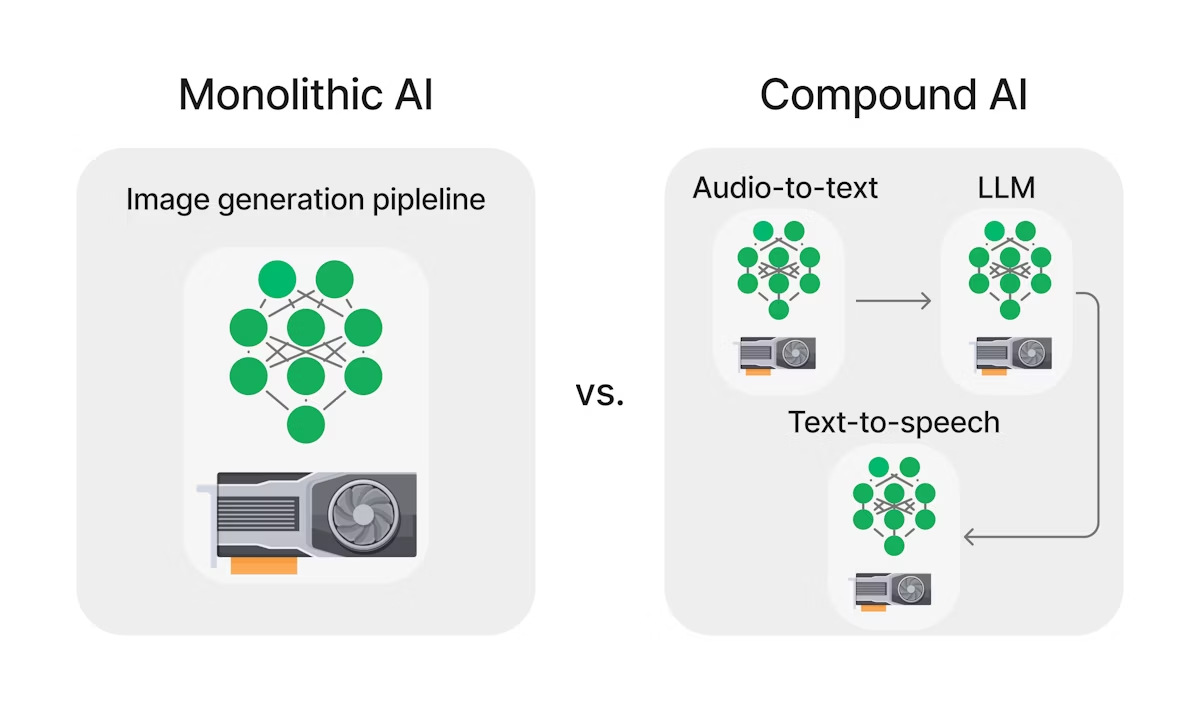
Traditional AI models operate independently, limited by the data they have been trained on. These models struggle to adapt without extensive retraining, making them inefficient for dynamic tasks.
For example, consider an AI model that needs to determine how many vacation days an employee has. If the model lacks access to the employee’s personal records, its response will be incorrect. However, by integrating AI with external databases and tools, we can design a system that retrieves and processes relevant data to provide accurate answers. This integration defines a compound AI system, which consists of multiple modular components working together to solve problems effectively.
System Design Principles
A compound AI system leverages modularity, where different components handle specific tasks:
- Language Models: Generate responses and structure data processing.
- Databases: Store and retrieve essential information.
- Programmatic Components: Ensure correctness, break down queries, and verify outputs.
- External Tools: Assist with calculations, searches, and data transformations.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a well-known example of a compound AI system. However, such systems are constrained by predefined control logic, limiting their flexibility when faced with novel queries.
AI Concepts: The Rise of AI Agents
What Are AI Agents?
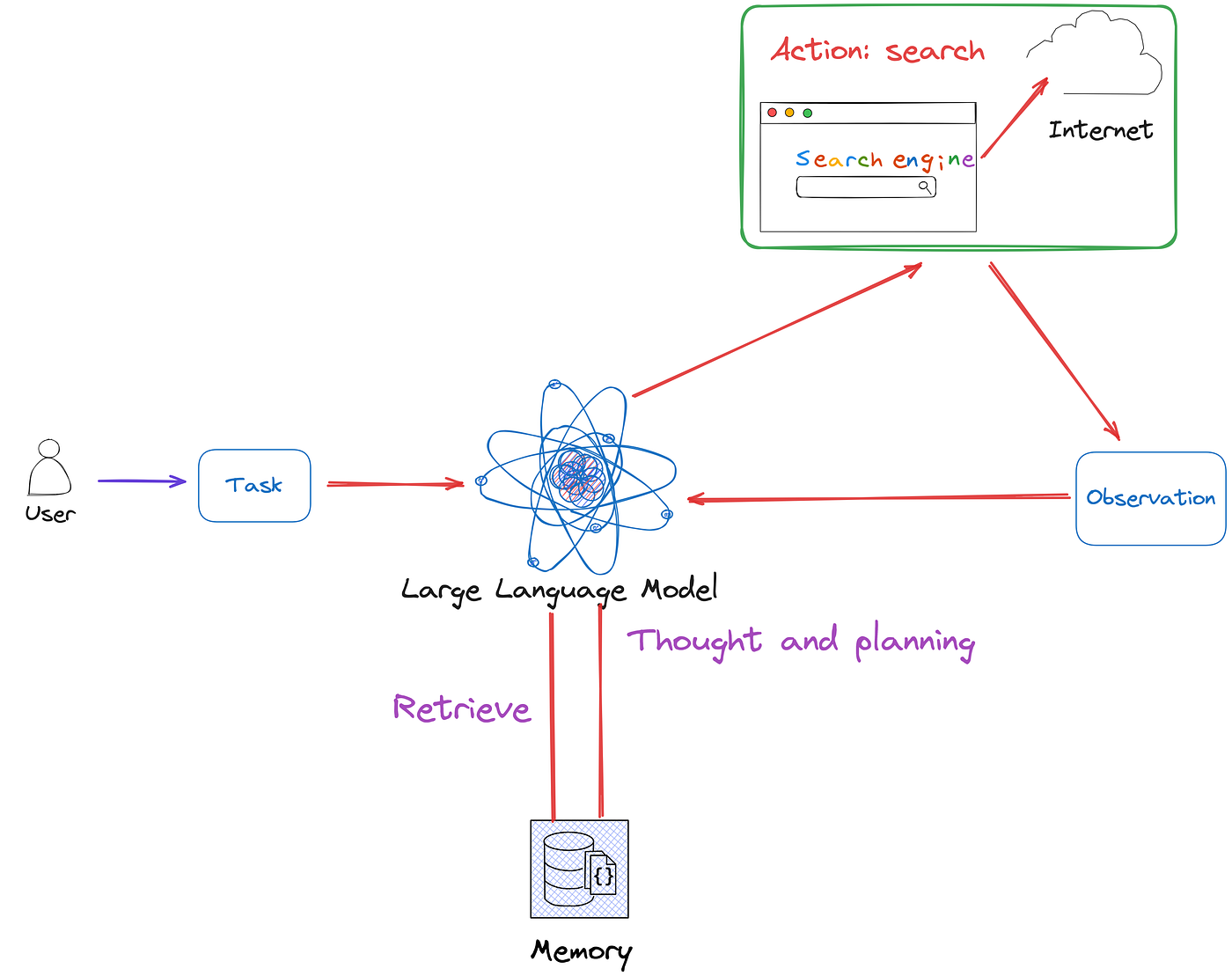
AI agents represent the next step in AI evolution by dynamically controlling the logic of compound AI systems. Instead of relying on static control mechanisms, AI agents use large language models (LLMs) to:
- Reason through complex problems.
- Plan and execute actions.
- Adapt based on iterative feedback.
Fast vs. Slow Thinking in AI Systems

AI agents operate along a spectrum of decision-making strategies:
- Fast Thinking: Rule-based execution with predefined logic, minimizing deviations.
- Slow Thinking: Adaptive problem-solving that involves planning, revising, and iterating to improve accuracy.
By placing LLMs in charge of control logic, AI agents can break down problems, request external assistance, and refine their responses over time.
Key Capabilities of AI Agents
- Reasoning: The ability to decompose complex queries into smaller, manageable tasks.
- Action Execution: Calling external tools (e.g., search engines, calculators, APIs) to retrieve or compute necessary information.
- Memory Utilization: Storing past interactions, reasoning steps, and relevant data to improve personalized responses.
ReACT: A Framework for AI Agents
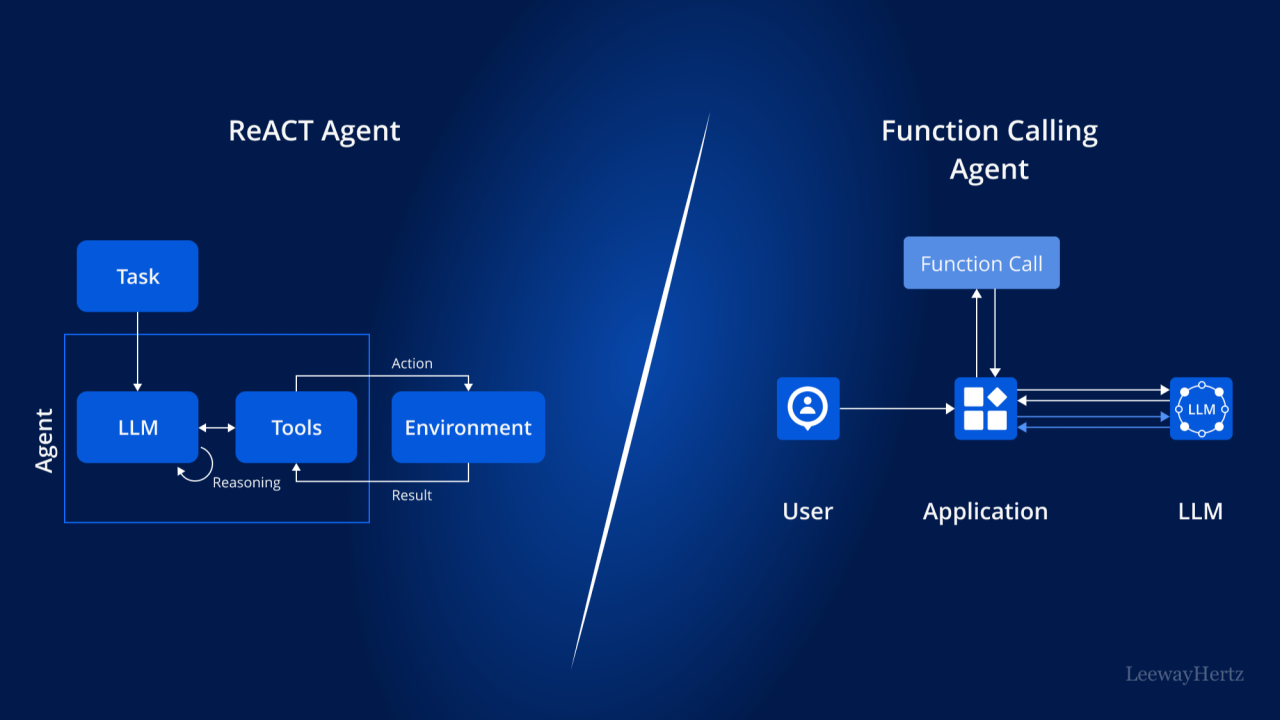
The ReACT framework (Reasoning + Acting) enables AI agents to make informed decisions iteratively:
- The user inputs a query.
- The AI agent reasons through the problem.
- The agent decides to act by calling external tools.
- It evaluates the response and adjusts the approach if needed.
By iterating this process, the AI agent ensures accurate and context-aware responses.
Technical Details
Example: AI Agent in a Vacation Planning Task
Let’s illustrate how an AI agent processes a query about vacation days:
class VacationAgent:
def __init__(self, llm, database, tools):
self.llm = llm # Language Model
self.database = database # Vacation Days Database
self.tools = tools # External APIs (weather, location, etc.)
def handle_query(self, query):
reasoning = self.llm.reason(query)
action_needed = self.llm.decide_action(reasoning)
if action_needed == "query_database":
data = self.database.fetch_user_vacation_days()
return f"You have {data} vacation days left."
elif action_needed == "check_weather":
weather = self.tools.fetch_weather()
return f"The weather forecast for your vacation is: {weather}."
else:
return "I cannot answer that query."
Workflow of AI Agent
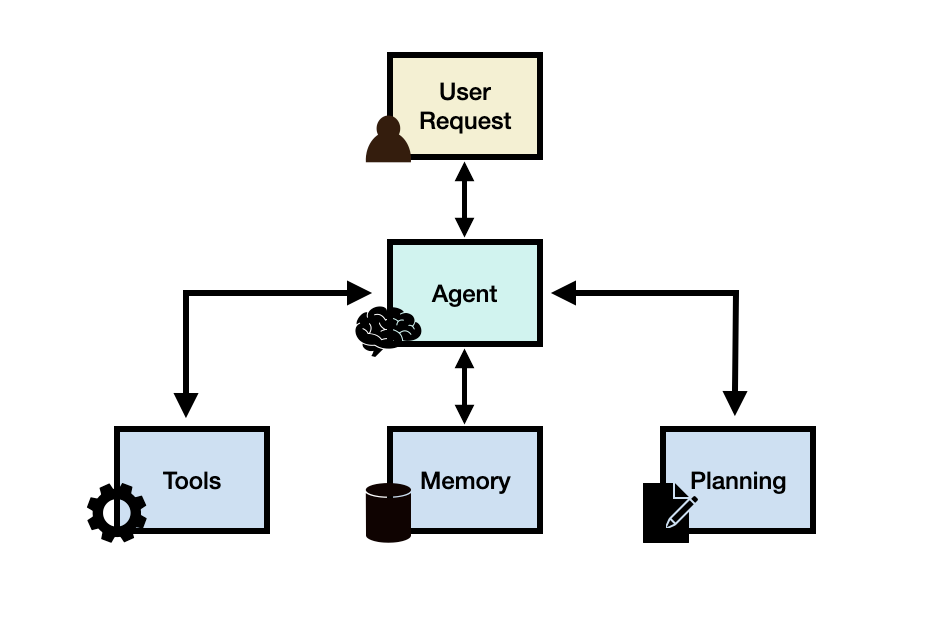
- User Query: “How many vacation days do I have?”
- Reasoning: The agent determines it needs to query a database.
- Action Execution: Fetches data from the vacation database.
- Response Generation: Constructs a user-friendly answer.
If a user asks about the weather, the agent dynamically adjusts by calling a weather API, showcasing its adaptability.
Conclusion
AI agents mark a paradigm shift in artificial intelligence by moving beyond static models toward dynamic, modular, and adaptive systems. By integrating reasoning, action execution, and memory, AI agents can tackle complex problems efficiently. The mathematical foundations of AI agents, including linear algebra, probability, and calculus, provide the theoretical underpinnings that drive their capabilities.